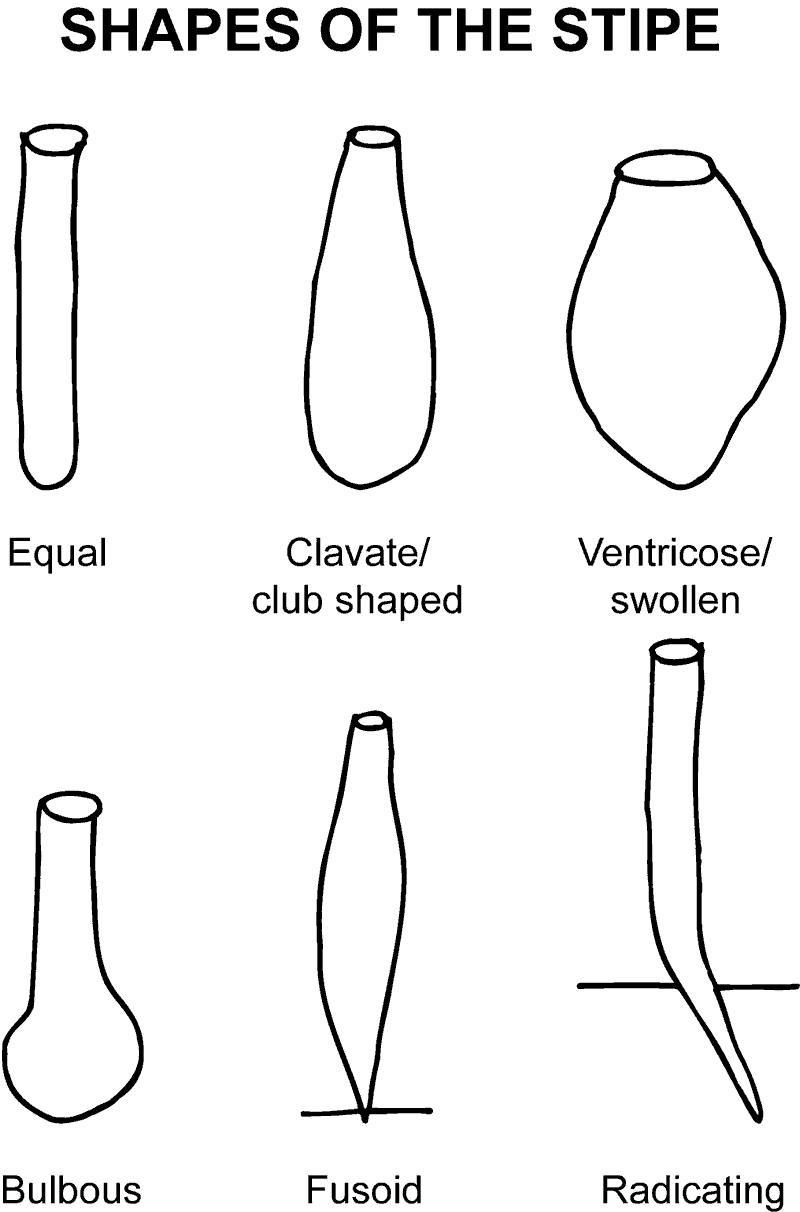https://www.mykoweb.com/articles/cultivation.html
The mushroom at the end of the world

- staying alive for every species requires livable collaboration
- scalability is not an ordinary feature of nature and requires a lot of work
- expect interactions between scalable and non-scalable projects
- The bulk of the work is threading through the non-scalable to reach the scalable
On the middle man
- a necessary consummate translator within the supply chain
- he maintains a mental map of who needs what
- helps efficiently route the inventory to the most suitable individual
On Freedom
- it is the concept of not having to be a cog in the machine.
- it does not necessarily lead to great economic outcome for the pursuing individual
- it allows the individual the ability to freely allocate the use of his time
The matsutake mushroom
- along most parts of supply chain it symbolizes a social exchange which strengthens social ties
- it is only during the sorting when the mushroom is looked at purely as a commodity
Man and nature
- The satoyama revitalization
- man is part of nature
- man’s disturbance to nature is part of nature
- unintentional design is the interplay of man and nature
- animal/human activities/disturbance
- pine tree growth
- matsutake mushroom colonization and growth
Insights from visit to far west fungi farm
On mushroom
-
Get woods chips from petco
-
Alder or ashpen shavings
-
6 inch to a foot at the bottom
-
Every few months 2 inch on the top
-
use Sundew, a carnivores plants to get rid of insects
-
Go to blue bottle cafe for burlap sacks
-
Don’t soak more spawns for more than 12 hours each time
-
If too dry soak, then keep in air for a day or two
- Drop some clay in water to detect chlorine in water used for soaking wood and spawn
Meetups
-
Oakland. Wednesday night
Useful resources
- LibGen.IO – site where free books can be downloaded
- sci-hub.tw – site where free research papers can be downloaded
- www.bloodhorse.com/horse-racing – site for horse racing statistics
- Far West Fungi Farm
Key take aways from California Mushrooms, the comprehensive identification guide

High level overview
The key features to use for mushroom identification
The steps prior to consuming
- See mushroom
- Collect entire mushroom
- cap
- stipe
- sections of the substrate / what it grows on
- note terrain its growing at
- make spore print overnight
- consult guidebook
- search for competing lookalikes that might be poisonous
- decide to eat it
- post eating – check for symptom of poisoning
- first symptoms can occur as early as 20mins into consumption
- if first symptom occurs only after 6 hours of consumption visit emergency room – you might have consumed an Amanitin containing variant and are about to DIE!!
- Galerina marginata
- Amanita phalloides, the Death Cap
- Amanita ocreata, the Destroying Angel
These ones will kill you for sure
Book Summary – Mycelium running

Usages
- antibiotics
- increasing immune system’s natural defense
- potential cure for HIV
- environment management
- mycofiltration: reduce risk of infection from sewage and effects of oil spill
- bioaccumulation: consolidates heavy metal
- Pest management: Cordyceps Metarhizium versus termites
Substrates
- Corn corbs
Insights
- diversity in fungal population directly correlated with strength and health of any ecosystem
- sensitive to dry contact. 1 layer of skin
References
- Growing gourmet and medicinal mushrooms, Paul Stamets
- The mushroom cultivator, Paul Stamets
- Medicinal mushrooms, Christopher Hobbs
- MycoMedicinals, Paul Stamets
- All the rain promises and more
- Mushrooms demystified
- Oyster mushroom cultivation, MushWorld
- Shiitake Mushroom Cultivation, MushWorld
- One Straw Revolution, Masanobu Fukuoka
- Permaculture: A practical guide for sustainable future, Mollison