Types of Risk
Process risks
- Definition Risk: Solving the wrong problem
- Scope Creep: Some projects are just big
- Complexity Risk: big projects have lots of edge cases
- Over-precision: Unwarranted or excessive certainty
- Priority Risk: Fluctuating relative importance
- Technical Risk: Code is basically a thousands of implicit assumptions despite best efforts to describe all possible corner cases
- Dependency Risk: Big projects stretch our coordination ability
Product risks
- Behavioral Risk: Customers don’t behave they way you expect
- Market Risk: External factors shape customer needs
People risk
- HiPPO Risk: Some decisions are made top-down when management does not understand actual ground situation
- Staffing Risk: Single point of failure, bus factor
- Impatience and Pressure: Sometimes we really want to be done so we take short cuts
- Ruinous Empathy: we are awfully nice to our colleagues, even when data states otherwise
- Stubbornness: we persist in making wrong decisions despite facts and reason stating otherwise
- Relationship Risk: My Team will hate me for making an unpopular decision that is correct
- Reputation Risk: This decision will impact my career
- Focus: Everything feels important
Causes
Humans are terrible at accessing risk
- Survival bias
- Availability bias
- Recency bias
- Anchoring bias
- Loss aversion – gains and losses asymmetry
Managing risk
- Work hard and know your customers
- Agonizing is expensive: time taken to agonize over which option of two is correct might be more than the actual time to validate the correctness of both options
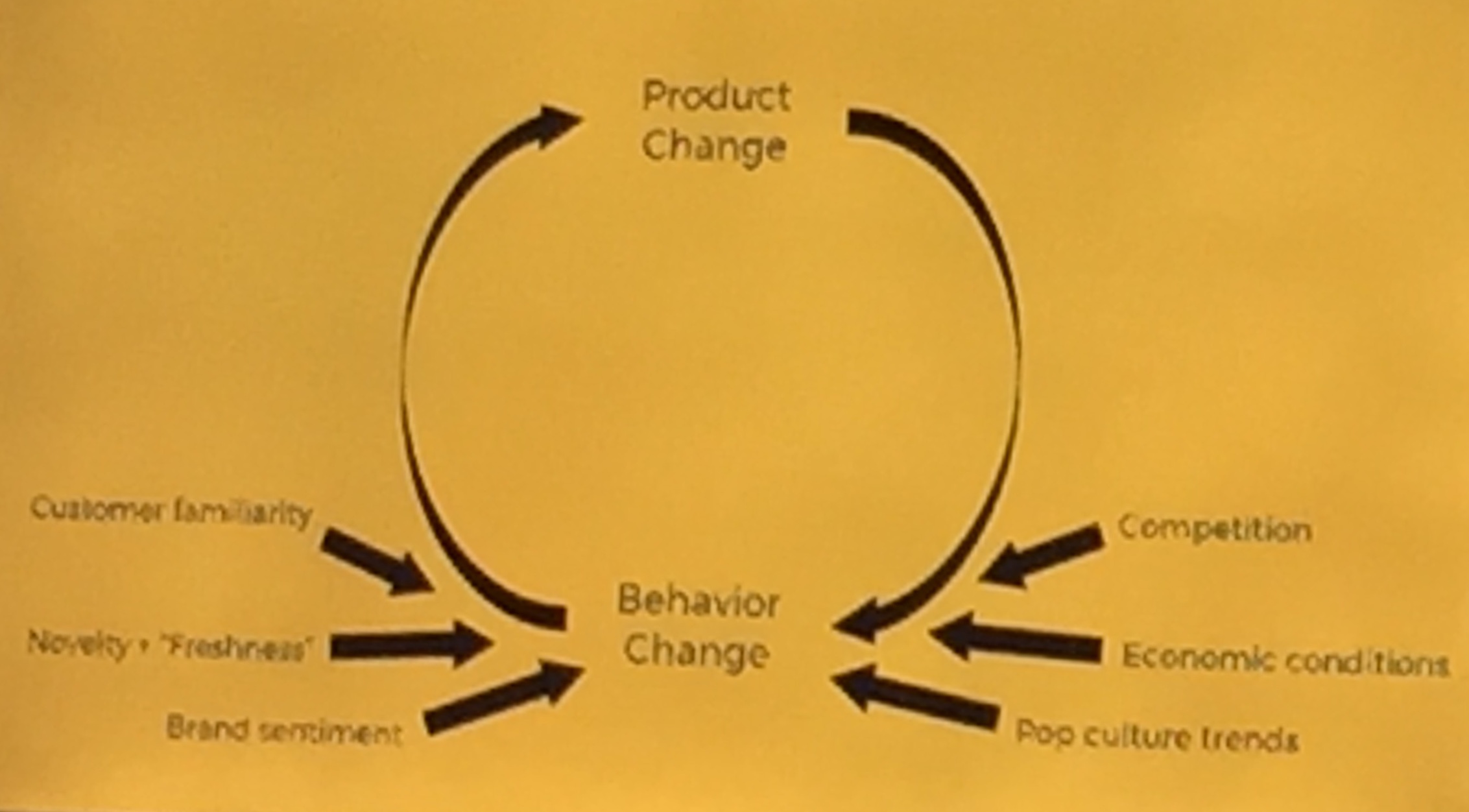
- Recognizing you are not running a closed system
- product change influences behavioral change
- behavioral change influences product change
- behavioral change is also influenced by
- competition
- economic conditions
- pop culture trends
- customer familiarity
- Novelty
- Brand sentiment
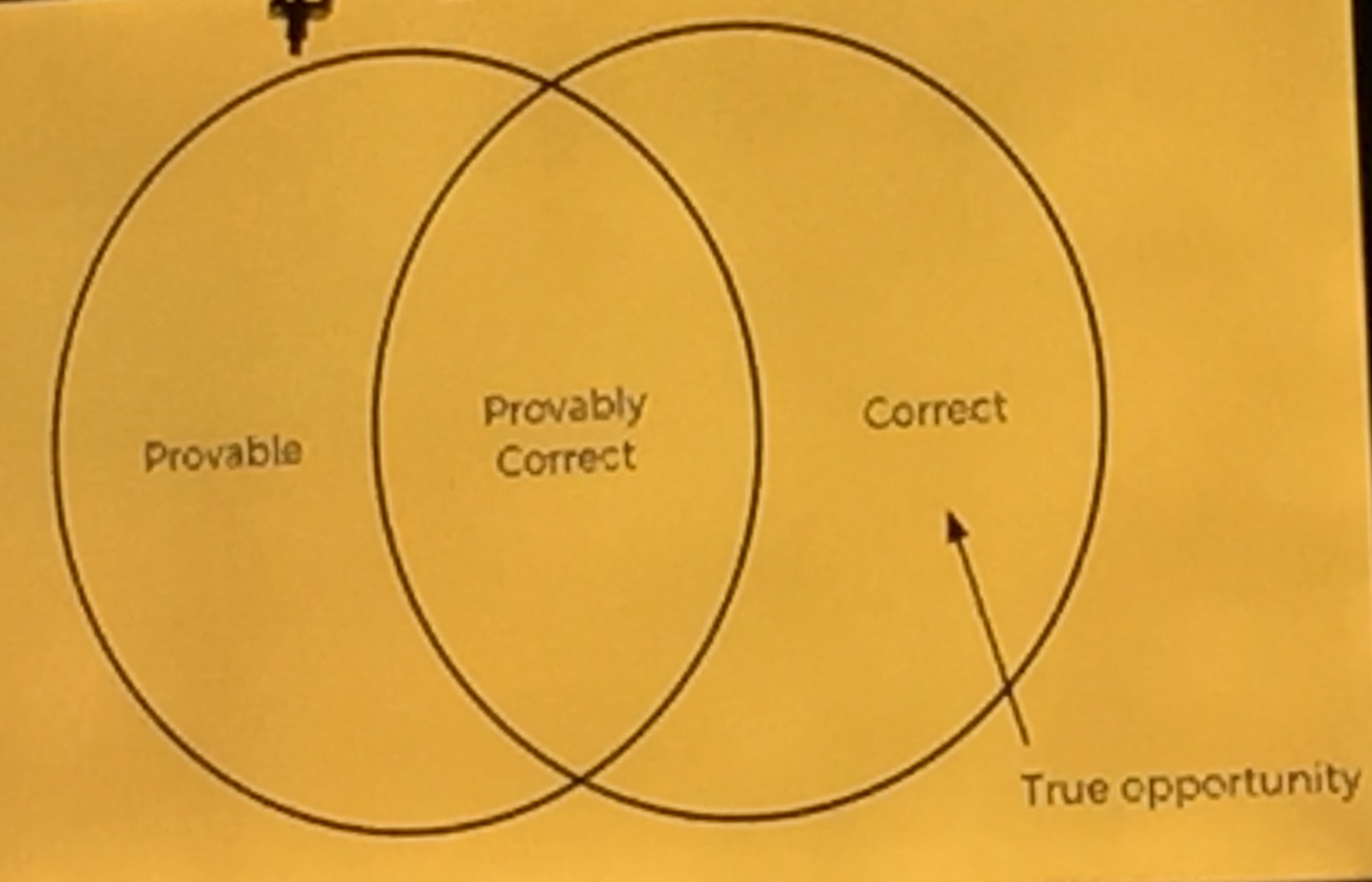
- Best ideas are not measurable
- There is only a small intersections between Provable and Correct
- True opportunity lies is usually Correct but not Provable
- Heuristics
- Focus: Decide what actually matters
- Agility: Reach quickly to new information
- Ambition: Chase big opportunities